Will Supply Chain Management Be Replaced by AI?
The supply chain world is changing fast. AI promises to automate everything from demand forecasting to logistics coordination. But will human expertise become obsolete?
AI will transform supply chain management but won’t completely replace human professionals. While AI excels at data processing and pattern recognition, complex decision-making, relationship management, and strategic planning still require human judgment and experience.

I’ve spent over 15 years helping global brands navigate China’s manufacturing landscape. During this time, I’ve watched technology reshape our industry. Yet the most successful partnerships still depend on human connections and nuanced understanding of market dynamics.
How Supply Chain Management Works?
Supply chains overwhelm most business owners. Multiple vendors, complex logistics, and quality control create constant headaches. Many entrepreneurs struggle to coordinate all these moving parts effectively.
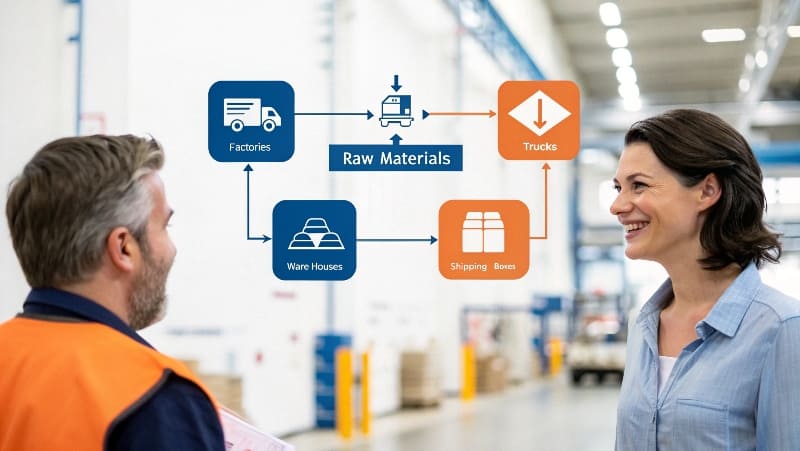
Supply chain management1 involves coordinating procurement, production, inventory, and distribution to deliver products efficiently. It requires balancing cost, quality, speed, and reliability across multiple suppliers and logistics partners.
[^2] process workflow diagram](https://feiliz.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Supply-chain-management-process-workflow-diagram.jpg)
Let me break down how modern supply chain management actually operates. The process starts with demand planning, where we analyze market trends and customer needs. Then comes supplier selection and relationship management2. This involves finding reliable manufacturers, negotiating contracts, and maintaining quality standards.
| Supply Chain Stage | Key Activities | Critical Success Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Planning | Demand forecasting, capacity planning | Market analysis, data accuracy |
| Sourcing | Supplier selection, contract negotiation | Relationship building, cost optimization |
| Manufacturing | Production oversight, quality control3 | Process monitoring, defect prevention |
| Logistics | Transportation, warehousing, distribution | Route optimization, inventory management |
| Customer Service | Order fulfillment, returns processing | Response time, satisfaction tracking |
The coordination between these stages requires constant communication and adjustment. When I work with Anna and other e-commerce sellers, I see how critical timing becomes. A delayed component can disrupt an entire product launch. Quality issues discovered late in production can cost thousands in rework and delays. This is why experienced supply chain professionals remain invaluable – we understand these interdependencies and know how to navigate complications.
Can AI Do Supply Chain Management?
Technology promises to solve every supply chain problem. AI tools claim they can predict demand, optimize inventory, and manage suppliers automatically. Business owners wonder if they need human experts anymore.
AI excels at data analysis, demand forecasting, and process optimization but cannot handle relationship management2, cultural nuances, and complex problem-solving that supply chain management requires.

AI brings powerful capabilities to supply chain operations. Machine learning algorithms can process vast amounts of historical data to predict demand patterns. Automated systems can track inventory levels and trigger reorders. Predictive analytics help identify potential disruptions before they occur.
| AI Capability | Supply Chain Application | Current Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Data Processing | Demand forecasting, trend analysis | Requires clean, accurate data inputs |
| Pattern Recognition | Quality defect detection, fraud prevention | Struggles with unprecedented situations |
| Optimization | Route planning, inventory management | Cannot account for relationship factors |
| Automation | Reordering, status updates | Lacks judgment for exceptions |
| Predictive Analytics | Risk assessment, disruption planning | Misses cultural and political nuances |
However, AI has significant limitations. When I negotiate with manufacturers in Shenzhen, success depends on understanding cultural context and building personal relationships. AI cannot navigate the subtle dynamics of Chinese business culture or adjust strategies based on a supplier’s facial expressions during negotiations. Complex problems often require creative solutions that combine technical knowledge with human intuition. A supplier’s financial difficulties might not show up in data until it’s too late, but experienced professionals can spot warning signs through personal interactions.
Is There a Future in Supply Chain Management?
Many professionals worry about job security as automation advances. Young people question whether supply chain careers offer long-term prospects. The uncertainty creates anxiety across the industry.
Supply chain management1 careers have a strong future, but professionals must adapt by developing skills in data analysis4, technology integration, and strategic thinking alongside traditional relationship management2 abilities.

The supply chain profession is evolving rather than disappearing. AI handles routine tasks, but this frees professionals to focus on strategic work. Successful supply chain managers now combine technical skills with relationship expertise. They interpret AI insights and make decisions based on broader business context.
| Traditional Skills | Emerging Skills | Future Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier relationships | Data interpretation | Strategic planning |
| Negotiation | Technology integration | Risk management |
| Quality control | Process automation | Innovation facilitation |
| Logistics coordination | Predictive analytics | Sustainability |
| Cost management | Digital transformation | Agility and resilience |
I see this transformation in my own work at Feiliz Tech. We use AI tools for demand forecasting and inventory optimization. But our clients still value our ability to understand their unique challenges and find creative solutions. When Anna faces a complex product development timeline, she needs someone who can coordinate multiple suppliers while managing quality requirements and budget constraints. This requires judgment that goes beyond what current AI can provide. The future belongs to professionals who leverage AI capabilities while maintaining the human skills that create real value.
Conclusion
AI will reshape supply chain management but won’t replace skilled professionals who adapt and combine technology with human expertise.
-
Understanding the fundamentals of supply chain management can help businesses optimize their operations. ↩ ↩
-
Explore the significance of relationship management in maintaining a successful supply chain. ↩ ↩ ↩
-
Find out how quality control can impact your supply chain efficiency and product quality. ↩
-
Understand the role of data analysis in optimizing supply chain processes and decision-making. ↩